我们思考一个问题:大语言模型是否能帮我们做更多的事情,比如帮我们发送邮件。默认情况下让大模型帮我们发送邮件,大模型会这样回复我们:
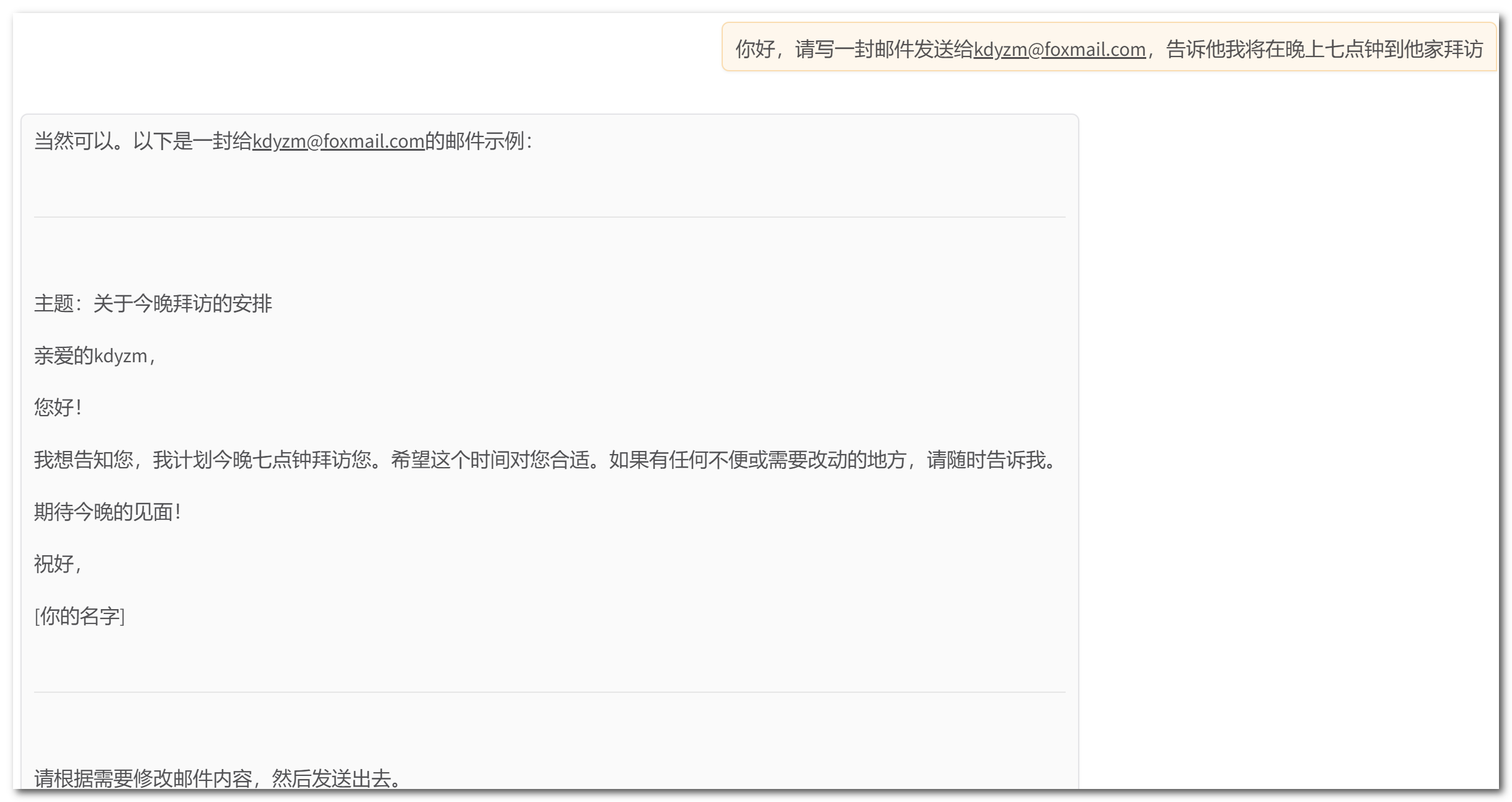
可以看到,大模型无法发送邮件,它只会帮我们生成一个邮件模板,然后让我们自己手动发送出去。如何让大模型拥有发送邮件的能力呢?这里就引入来了一个概念:function calling。
一、概念:Function calling
简单来说,Function calling让大语言模型拥有了调用外部接口的能力,使用这种能力,大模型能做一些比如实时获取天气信息、发送邮件等和现实世界交互的事情。
1、原理
在发送信息给大模型的时候,携带着“工具”列表,这些工具列表代表着大模型能使用的工具。当大模型遇到用户提出的问题时,会先思考是否应该调用工具解决问题,如果需要调用工具,和普通消息不同,这种情况下会返回“function_call”类型的消息,请求方根据返回结果调用对应的工具得到工具输出,然后将之前的信息加上工具输出的信息一起发送给大模型,让大模型整合起来综合判断给出结果。
以获取天气信息为例,官网给出了获取天气的流程图
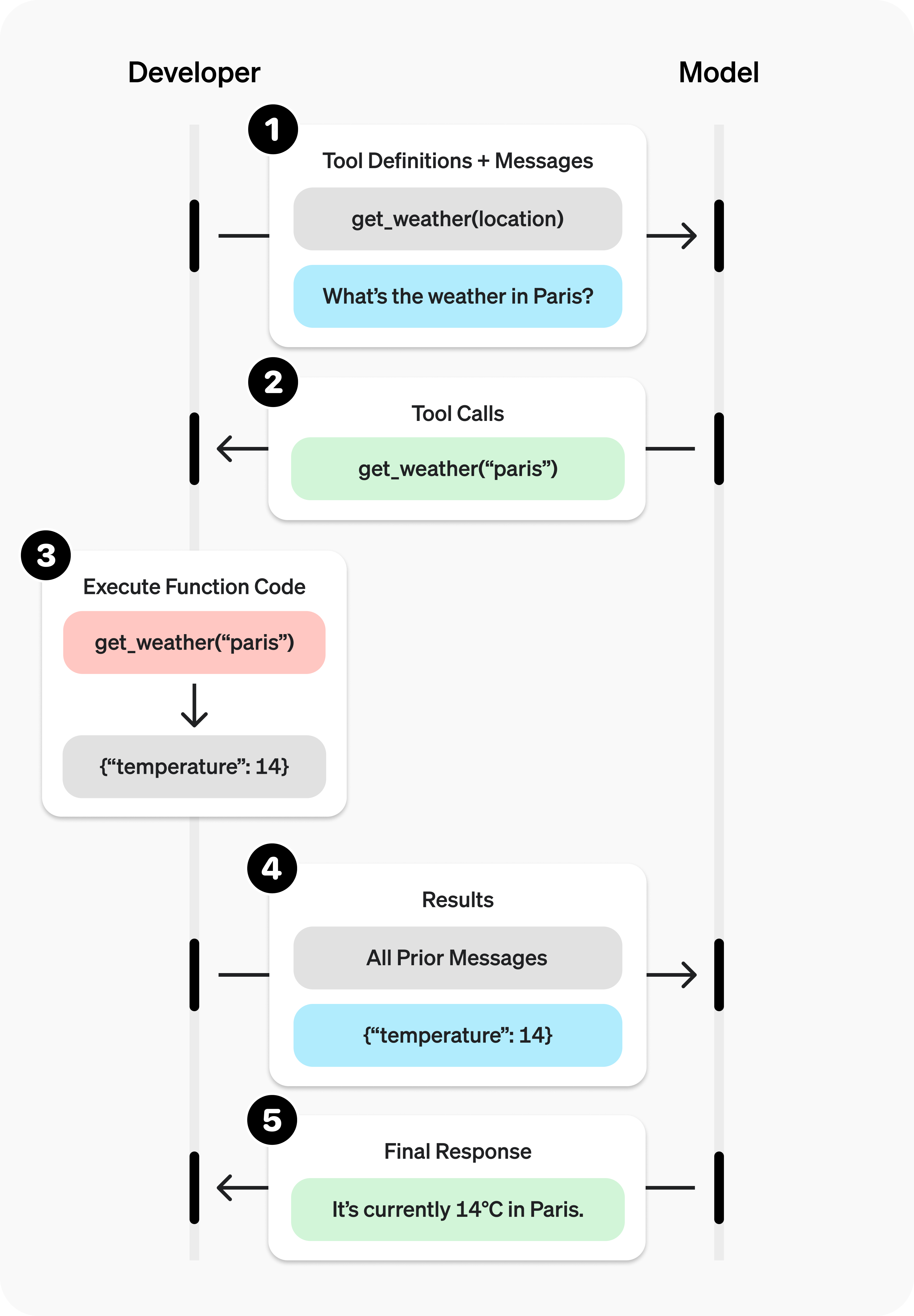
2、案例
OpenAI官网Function calling文档:https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/function-calling?api-mode=responses&example=get-weather
文档中给了获取天气、发送邮件、搜索本地知识库这三个例子,以获取天气为例:
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI()
tools = [{
"type": "function",
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "Get current temperature for a given location.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "City and country e.g. Bogotá, Colombia"
}
},
"required": [
"location"
],
"additionalProperties": False
}
}]
response = client.responses.create(
model="gpt-4o",
input=[{"role": "user", "content": "What is the weather like in Paris today?"}],
tools=tools
)
print(response.output)
结果输出:
[{
"type": "function_call",
"id": "fc_12345xyz",
"call_id": "call_12345xyz",
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": "{\"location\":\"Paris, France\"}"
}]
可以看到,使用OpenAI的官方API调用很繁琐,而且定义工具列表需要使用json格式的字符串,非常的不友好,lagnchain则解决了这些麻烦。
二、langchain中的Tool calling
langchain中的Function calling换了个更直接的名字:Tool calling,翻译过来叫做“工具调用”,实际上底层还是使用的Function calling。
Tools概念:https://python.langchain.com/docs/concepts/tools/
Tool calling概念:https://python.langchain.com/docs/concepts/tool_calling/
1、工具定义
定义工具很简单,使用装饰器@tool,比如定义两数相乘的工具如下:
from langchain_core.tools import tool
@tool
def multiply(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Multiply two numbers."""
return a * b
可以看到,定义一个工具方法很简单,普通方法加上装饰器@tool即可(关于复杂方法后续再讲)。
工具定义完成,可以使用
print(
json.dumps(
multiply.args_schema.model_json_schema(),
indent=4,
ensure_ascii=False,
)
)
打印scheme信息:
{
"description": "Multiply two numbers.",
"properties": {
"a": {
"title": "A",
"type": "integer"
},
"b": {
"title": "B",
"type": "integer"
}
},
"required": [
"a",
"b"
],
"title": "multiply",
"type": "object"
}
2、工具调用
上面我们已经定义好了两数相乘的工具:
from langchain_core.tools import tool
@tool
def multiply(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Multiply two numbers."""
return a * b
接下来使用携带该工具访问大模型:
# Tool 创建
tools = [multiply]
# Tool 绑定
model_with_tools = model.bind_tools(tools)
# Tool 调用
response = model_with_tools.invoke("2乘以2等于多少?")
输出大模型返回的function_tool信息:
print(json.dumps(response.tool_calls, indent=4))
结果如下所示:
[
{
"name": "multiply",
"args": {
"a": 2,
"b": 3
},
"id": "chatcmpl-tool-83c83e9537ae4820bc3b1123fec3570b",
"type": "tool_call"
}
]
它告诉我们要调用multiply方法,参数是a=2和b=3,如何调用呢?
3、工具执行
大模型已经告诉我们要执行的方法以及调用的参数了,接下来如何执行呢?
第一步:转换tool列表为字典
tool_dic = {tool.name: tool for tool in tools}
第二步:依次执行tool_call列表中的方法
for tool_call in response.tool_calls:
selected_tool = tool_dic[tool_call["name"].lower()]
tool_msg = selected_tool.invoke(tool_call)
print(type(tool_msg))
这样就可以执行目标方法了。注意这里返回的tool_msg信息类型是ToolMessage。
接下来需要将上下文信息带着最后输出的工具输出的信息一起打包给大模型,让大模型整合结果输出给出最终答案。
4、整合到大模型
调用完工具之后需要将结果告诉大模型,让大模型综合上下文得到后续答案。如何告诉大模型呢?在上一篇文章《大模型开发之langchain0.3(二):构建带有记忆功能的聊天机器人》中告诉大模型上下文,也即是历史记录的方法就是构造Message列表,上一步工具执行的结果返回类型是ToolMessage,我们将它加入列表即可;最后将message列表一起发送给大模型,让大模型给出答案。
完整代码如下所示:
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage
from langchain_core.tools import tool
@tool
def multiply(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Multiply a and b."""
print("multiply 方法被执行")
return a * b
model = init_chat_model("gpt-3.5-turbo")
# Tool 创建
tools = [multiply]
# Tool 绑定
model_with_tools = model.bind_tools(tools)
# Tool 调用
history = [HumanMessage("2乘以3等于多少?")]
ai_message = model_with_tools.invoke(history)
history.append(ai_message)
tool_dic = {tool.name: tool for tool in tools}
for tool_call in ai_message.tool_calls:
selected_tool = tool_dic[tool_call["name"].lower()]
tool_msg = selected_tool.invoke(tool_call)
history.append(tool_msg)
ai_message = model_with_tools.invoke(history)
print(ai_message.content)
if __name__ == '__main__':
pass
结果:
multiply 方法被执行
2乘以3等于6。
三、整合gradio
为了更直观的查看工具调用的情况,将本节内容整合到gradio是个不错的选择,同时需要兼容上篇文章《大模型开发之langchain0.3(二):构建带有记忆功能的聊天机器人》中记忆功能、Context Window限制功能,由于使用了工具调用,暂时没想好如何实现工具调用显示和正文部分流式输出的组合。
1、代码整合
核心点在于如何显示方法调,可以参考文档:https://www.gradio.app/docs/gradio/chatbot#demos 案例中的chatbot_with_tools 章节。
from gradio import ChatMessage
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage, AIMessage, trim_messages
from langchain_core.tools import tool
import gradio as gr
@tool
def multiply(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Multiply a and b."""
print("multiply 方法被执行")
return a * b
model = init_chat_model("gpt-3.5-turbo")
# Tool 创建
tools = [multiply]
# Tool 绑定
model_with_tools = model.bind_tools(tools)
trimmer = trim_messages(
max_tokens=300,
strategy="last",
token_counter=model,
include_system=True,
allow_partial=False,
start_on="human",
)
def response(input_message, gradio_history):
# Tool 调用
history = [HumanMessage(i["content"]) if i["role"] == 'user' else AIMessage(i["content"]) for i in gradio_history]
history.append(HumanMessage(input_message))
local_gradio_history = list()
ai_message = model_with_tools.invoke(trimmer.invoke(history))
if ai_message.tool_calls:
tool_dic = {tool_item.name: tool_item for tool_item in tools}
for tool_call in ai_message.tool_calls:
tool_name = tool_call["name"].lower()
selected_tool = tool_dic[tool_name]
tool_msg = selected_tool.invoke(tool_call)
history.append(tool_msg)
local_gradio_history.append(
ChatMessage(
role="assistant",
content=f"tool '{tool_name}' invoke result is {tool_msg}",
metadata={"title": f"🛠️ Used tool '{tool_name}'"},
)
)
yield local_gradio_history
ai_message = model_with_tools.invoke(trimmer.invoke(history))
local_gradio_history.append(
ChatMessage(
role="assistant",
content=ai_message.content,
)
)
yield local_gradio_history
demo = gr.ChatInterface(
fn=response,
type="messages",
flagging_mode="manual",
flagging_options=["Like", "Spam", "Inappropriate", "Other"],
save_history=True,
)
if __name__ == '__main__':
demo.launch()
2、运行界面
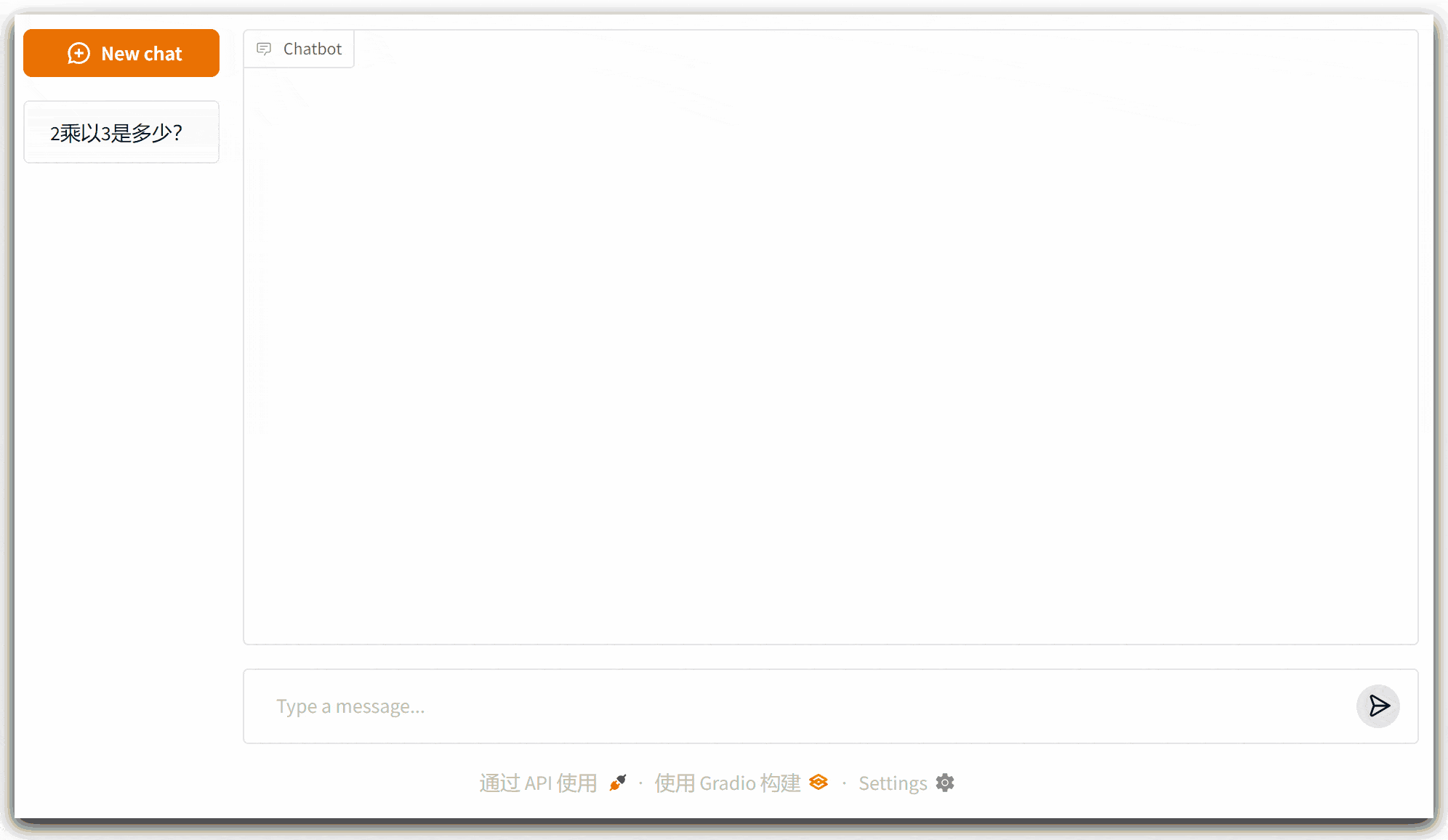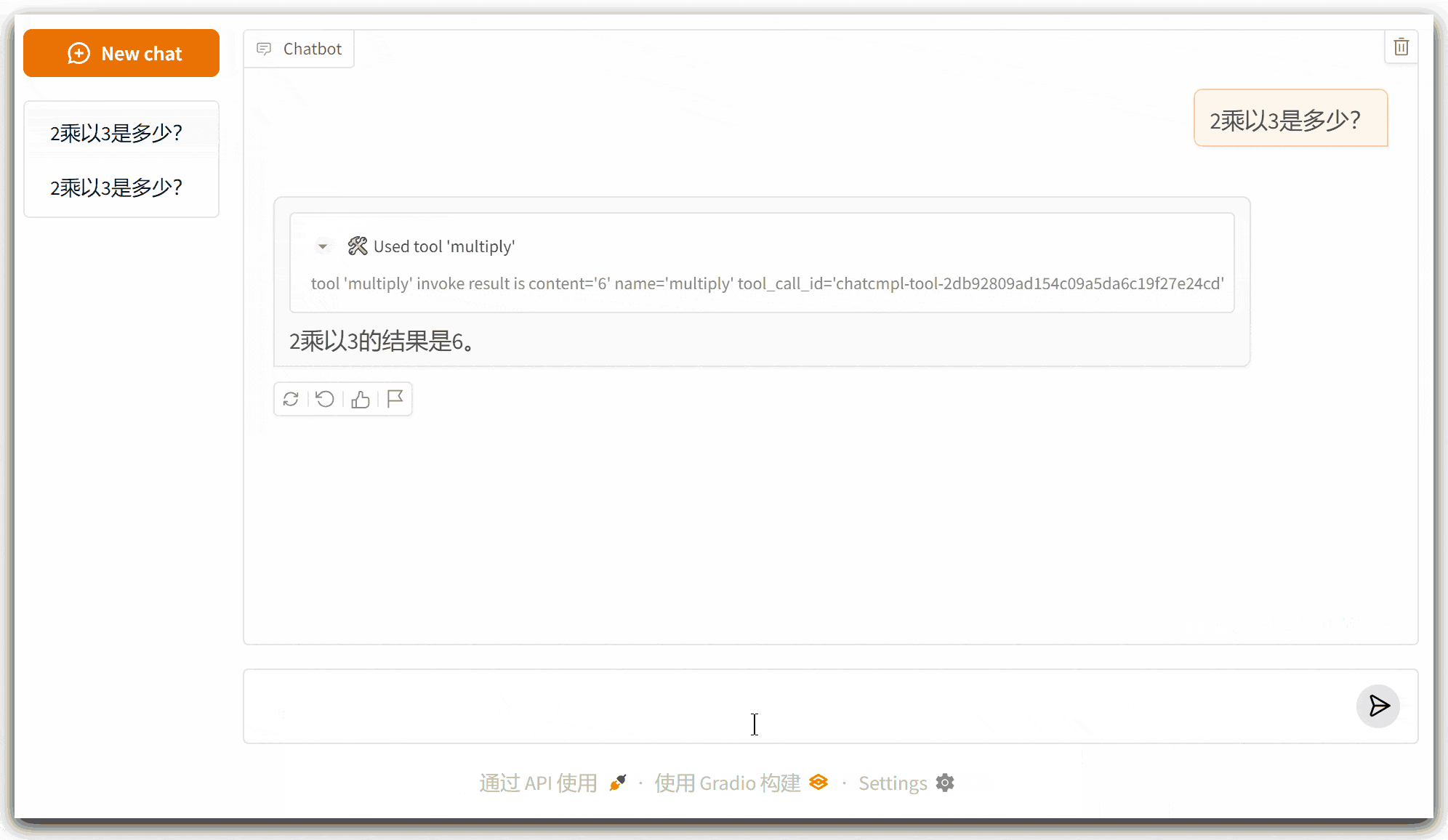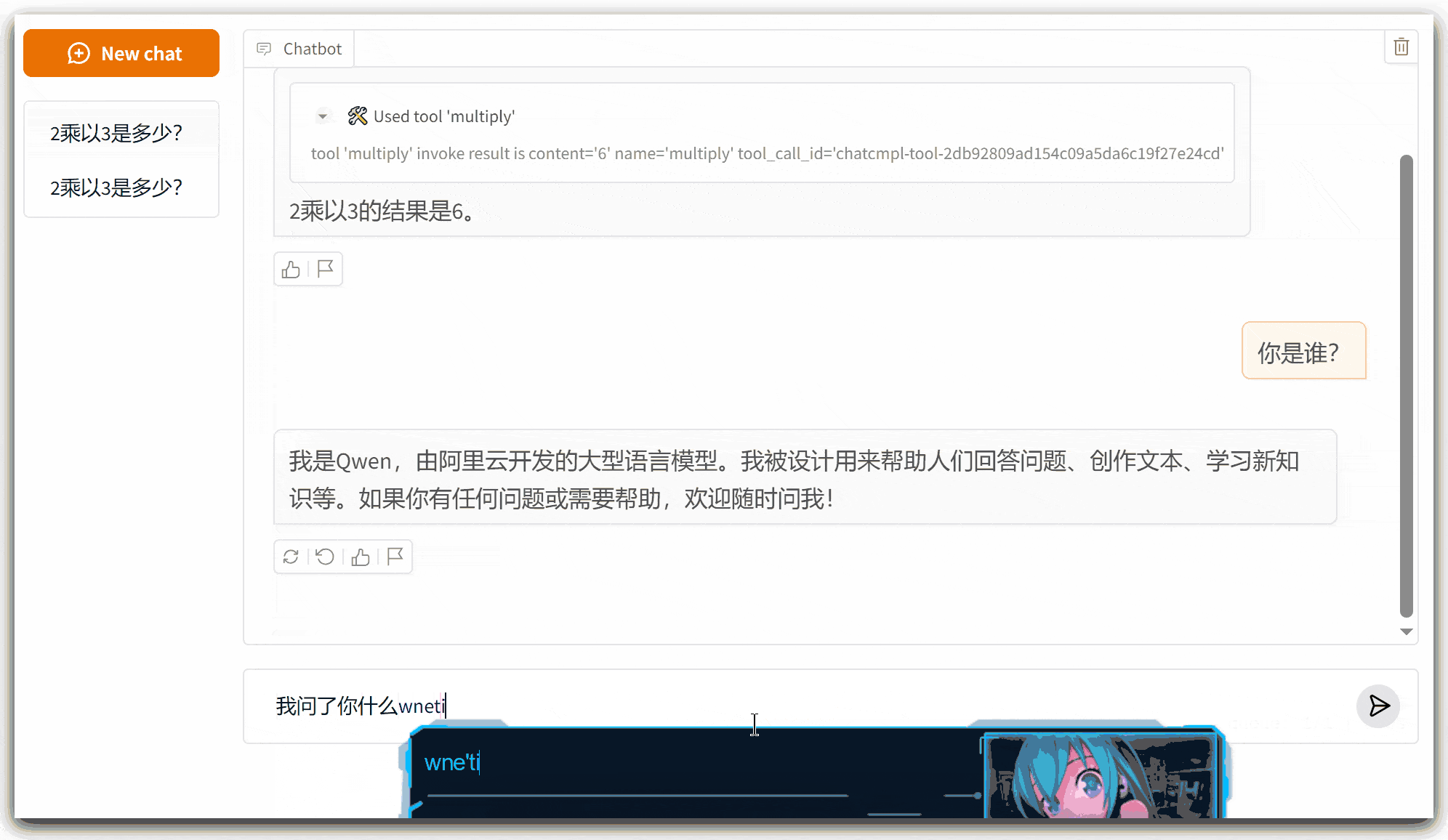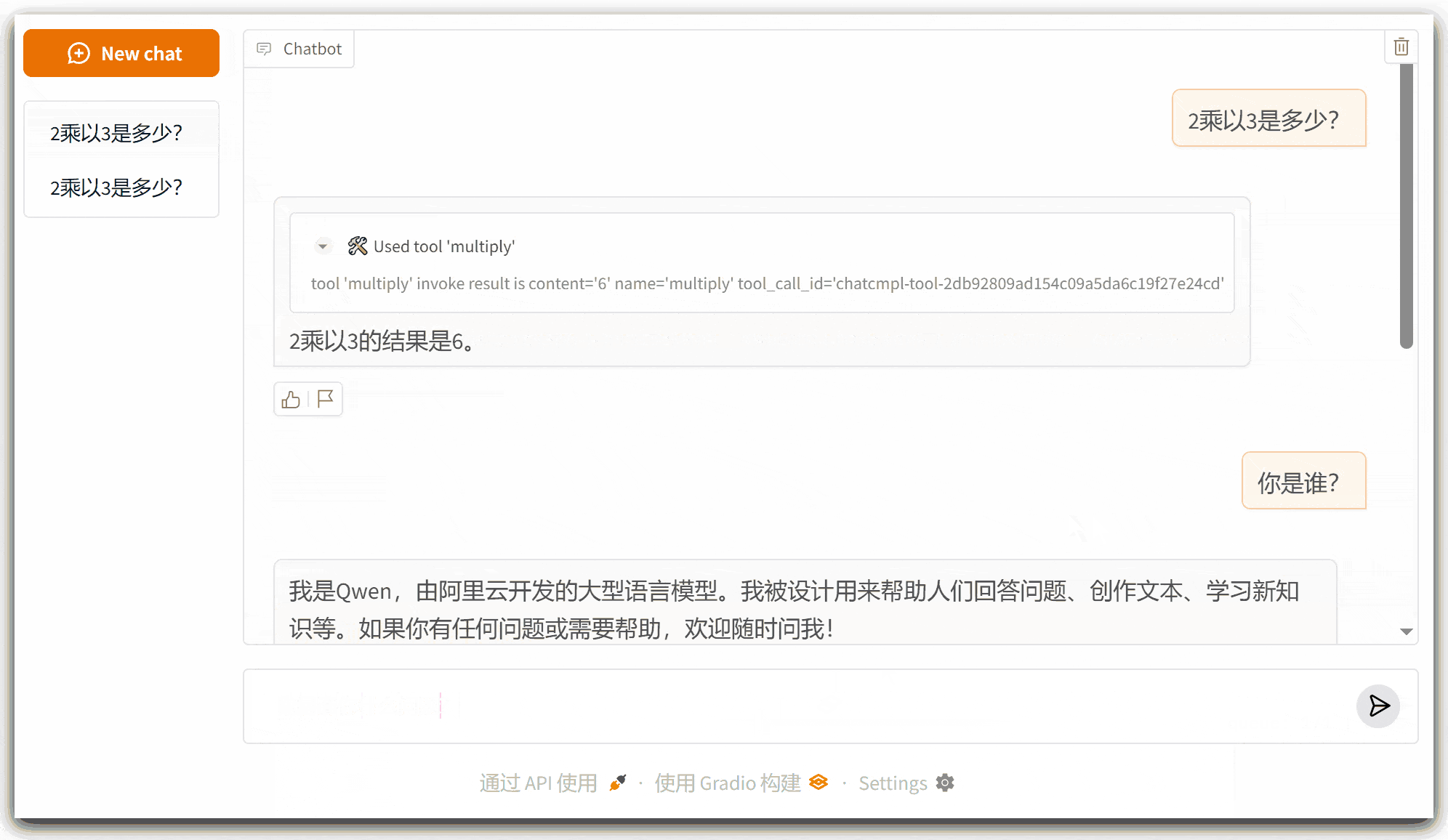
四、注意事项
注意,并非所有的大模型都支持function_call,不支持function_call的大模型输出返回的AIMessage的tool_calls字段一直是空的。
注意:本文归作者所有,未经作者允许,不得转载