本篇文章讨论下如何添加“人机交互(human-in-the-loop)”动作到方法调用的流程中,翻译成大白话,就是怎样手动干预方法调用。
在之前的文章《大模型开发之langchain0.3(三):方法调用》中,已经说明了大模型会根据提示词信息自己决定调用什么方法,现在不直接调用方法了,在调用方法前,必须先得到我的同意才行。如何实现该功能呢?
一、方法调用中人机交互原理
我们先回顾下方法调用的原理:
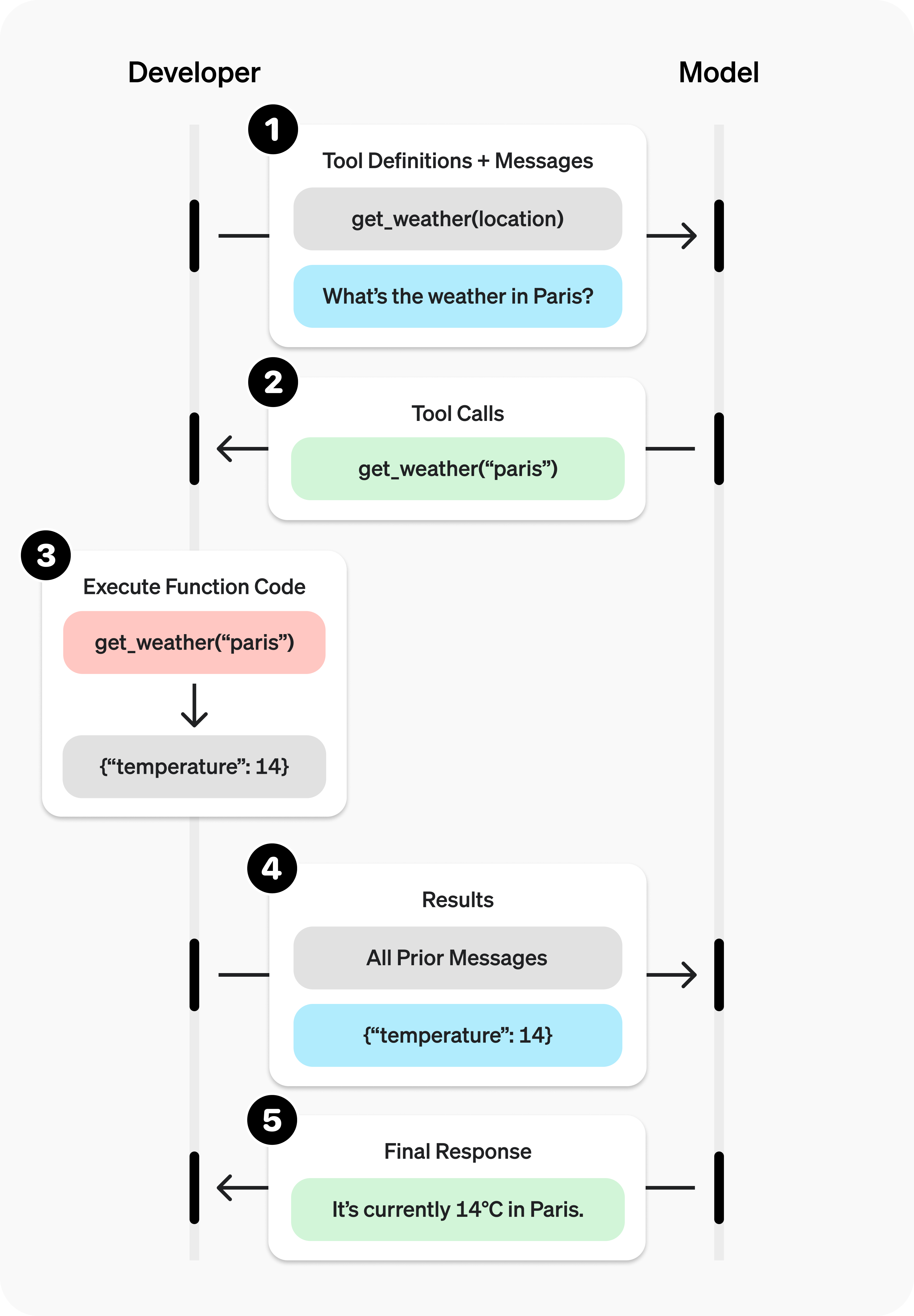
上图中,在❷处大模型告诉用户应该调用什么方法;用户在❸处执行方法调用。我们在❷和❸之间加上审核的逻辑,就可以干预方法执行了。
二、CLI人机交互实现
代码实现如下:
import json
from typing import List, Dict
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
from langchain_core.messages import AIMessage
from langchain_core.tools import tool
class NotApproved(Exception):
"""Custom exception."""
def human_approval(msg: AIMessage) -> AIMessage:
"""Responsible for passing through its input or raising an exception.
Args:
msg: output from the chat model
Returns:
msg: original output from the msg
"""
tool_strs = "\n\n".join(
json.dumps(tool_call, indent=4) for tool_call in msg.tool_calls
)
input_msg = (
f"Do you approve of the following tool invocations\n\n{tool_strs}\n\n"
"Anything except 'Y'/'Yes' (case-insensitive) will be treated as a no.\n >>>"
)
resp = input(input_msg)
if resp.lower() not in ("yes", "y"):
raise NotApproved(f"Tool invocations not approved:\n\n{tool_strs}")
return msg
def call_tools(msg: AIMessage) -> List[Dict]:
"""Simple sequential tool calling helper."""
tool_map = {tool.name: tool for tool in tools}
tool_calls = msg.tool_calls.copy()
for tool_call in tool_calls:
tool_call["output"] = tool_map[tool_call["name"]].invoke(tool_call["args"])
return tool_calls
@tool
def count_emails(last_n_days: int) -> int:
"""Dummy function to count number of e-mails. Returns 2 * last_n_days."""
return last_n_days * 2
@tool
def send_email(message: str, recipient: str) -> str:
"""Dummy function for sending an e-mail."""
return f"Successfully sent email to {recipient}."
if __name__ == '__main__':
llm = init_chat_model("gpt-4o-mini", model_provider="openai")
tools = [count_emails, send_email]
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools)
chain = llm_with_tools | human_approval | call_tools
try:
result = chain.invoke("how many emails did i get in the last 5 days?")
print(json.dumps(result, indent=4))
except NotApproved as e:
print()
print(e)
以上代码是官方给出的控制台版本代码案例,通过构建chain调用链,在中间加上human_approval逻辑实现人工干预方法调用;如果输入Y/Yes之外的字符,将会抛出异常中断调用链的后续执行:

如果输入Y,则会输出带有output字段的tool_call信息:

三、langchain人机交互的局限性
本篇文章案例来自于官方网站:https://python.langchain.com/docs/how_to/tools_human/
官方网站在开头就明确说了:强烈建议使用langgraph实现人机交互功能,详情参考:https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/concepts/human_in_the_loop/
从以上代码中已经可以看得出直接基于langchain的方法调用实现人机交互还是挺麻烦的,方法调用要手动调用,手动处理结果等,使用langgraph几乎能全自动解决所有问题。
END.
注意:本文归作者所有,未经作者允许,不得转载